
Notes on “Globalization and All That” Class No. 7
Links to Other Classes
Prev Class: No. 6 — Index
Preliminaries
Reminder: Helter Skelter: A Presentation and Discussion on the Beatles’ White Album and the Impact of 1968
- Thursday, November 8, 2018
- 5:00 to 7:00 PM
- Lowell Telecommunications, 246 Market St., Lowell
- FREE!
Development and Global Inequality
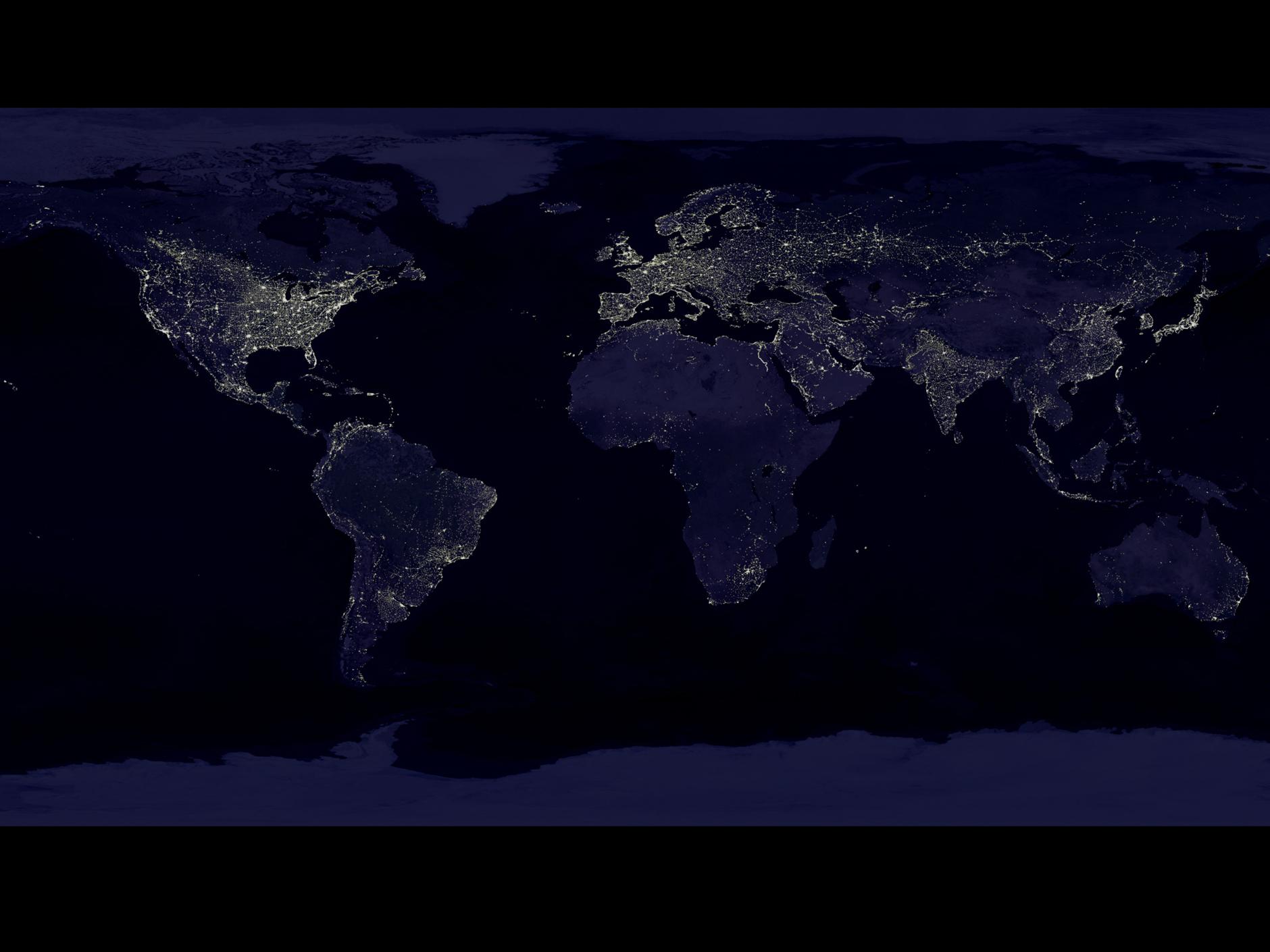
Inequality has actually been decreasing in the world — slides
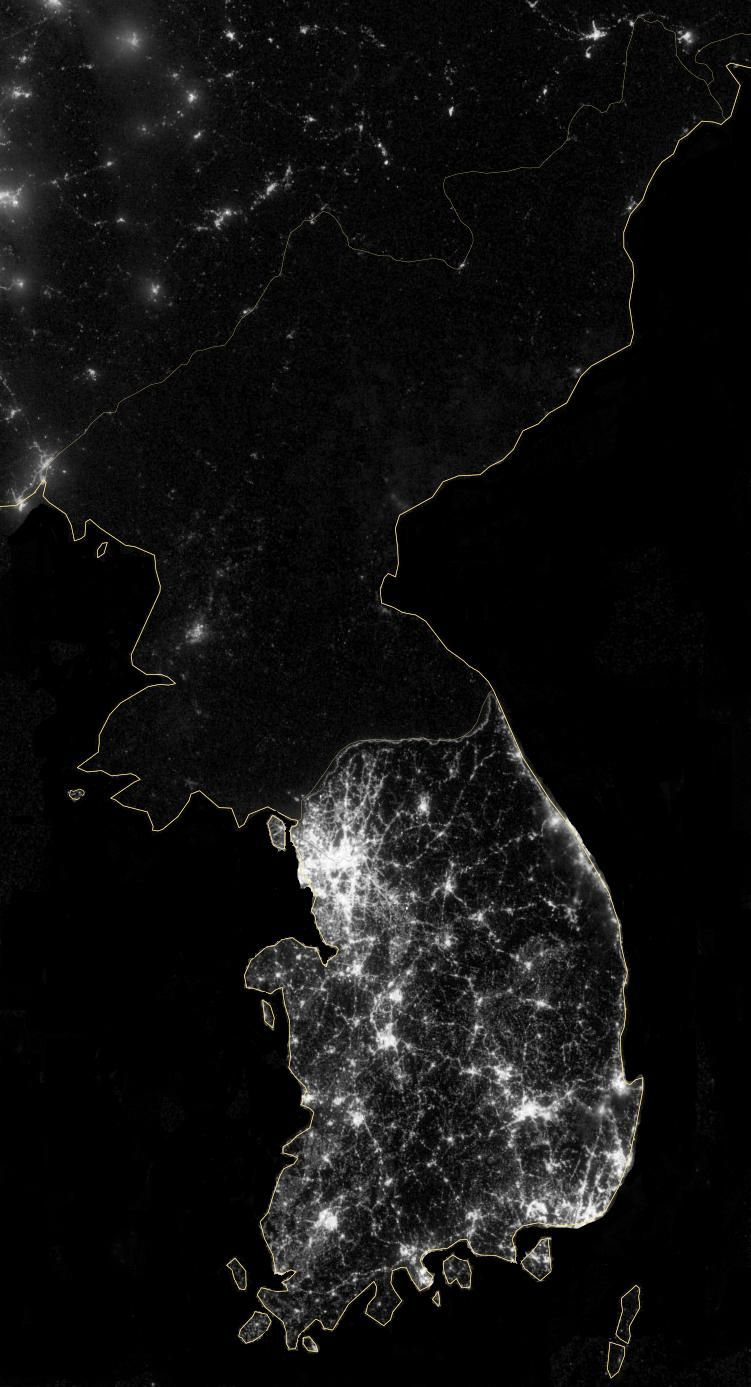
- North and South Korea at Night
What would you do if you were the President of a poor country?
- education
- infrastructure — requires capital
So how to attract capital?
- stabilize government
- root out corruption
- make peace with neighboring countries
Global Inequalities
- 54% of the world’s population lives on less than $1/day
Growth reduces poverty...
United Nations Millennium Development Goals [reference: Wikipedia]
- To eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
- To achieve universal primary education
- To promote gender equality and empower women
- To reduce child mortality
- To improve maternal health
- To combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases
- To ensure environmental sustainability
- To develop a global partnership for development
Types of Poverty
- Absolute
- Relative
- Subjective — actual income compared with income earner’s expectations
Per capita income by country
Characteristics of Developing Nations
- lack of a tax base
- poor infrastructure
- cell phone towers & drone delivery somewhat circumvent this problem
- poor education systems
- extreme regionalism
- prohibitive value systems pitting one group against another
- very little national cohesion
- traditional female roles
- long period of colonialism (independence only came in the late 20th century)
- still maintain their dependence on former colonial powers
Human Development Index (HDI)
Criteria for measuring a country’s level of development
- life expectancy
- education
- living standards
The Triumphs and Tragedies of Globalization
- International trade and investment have increased rapidly.
- ...
Many people oppose globalization because...
- inequality between rich and poor countries remains and is decreasing, but slowly
- it may be hurting local cultures and the natural environment
- some suggest that globalization is a form of imperialism, which is the economic domination of one country by another
- it contributes to the “homogenization” of the world, the cultural domination of less powerful by more powerful countries
World’s Poorest Countries [reference: Wikipedia]
| Rank |
|
Country |
|
Per
capita
income |
|
Year |
| 168 |
|
 Chad Chad |
|
$ 2,400 |
|
2017 est. |
| 169 |
|
 Uganda Uganda |
|
2,400 |
|
2017 est. |
| 170 |
|
 Zimbabwe Zimbabwe |
|
2,300 |
|
2017 est. |
| 171 |
|
 Yemen Yemen |
|
2,300 |
|
2017 est. |
| 172 |
|
 Mali Mali |
|
2,200 |
|
2017 est. |
| 173 |
|
 Benin Benin |
|
2,200 |
|
2017 est. |
| 174 |
|
 Rwanda Rwanda |
|
2,100 |
|
2017 est. |
| 175 |
|
 Ethiopia Ethiopia |
|
2,100 |
|
2017 est. |
| 176 |
|
 Solomon Islands Solomon Islands |
|
2,100 |
|
2017 est. |
| 177 |
|
 Guinea Guinea |
|
2,000 |
|
2017 est. |
| 178 |
|
 Burkina Faso Burkina Faso |
|
1,900 |
|
2017 est. |
| 179 |
|
 Kiribati Kiribati |
|
1,900 |
|
2017 est. |
| 180 |
|
 Afghanistan Afghanistan |
|
1,900 |
|
2017 est. |
| 181 |
|
 Sierra Leone Sierra Leone |
|
1,800 |
|
2017 est. |
| 182 |
|
 Guinea-Bissau Guinea-Bissau |
|
1,800 |
|
2017 est. |
| 183 |
|
 Haiti Haiti |
|
1,800 |
|
2017 est. |
| 184 |
|
 North Korea North Korea |
|
1,700 |
|
2015 est. |
| 185 |
|
 The Gambia The Gambia |
|
1,700 |
|
2017 est. |
| 186 |
|
 Togo Togo |
|
1,600 |
|
2017 est. |
| 187 |
|
 Madagascar Madagascar |
|
1,600 |
|
2017 est. |
| 188 |
|
 Comoros Comoros |
|
1,600 |
|
2017 est. |
| 189 |
|
 South Sudan South Sudan |
|
1,500 |
|
2017 est. |
| 190 |
|
 Eritrea Eritrea |
|
1,400 |
|
2017 est. |
| 191 |
|
 Mozambique Mozambique |
|
1,300 |
|
2017 est. |
| 192 |
|
 Niger Niger |
|
1,200 |
|
2017 est. |
| 193 |
|
 Malawi Malawi |
|
1,200 |
|
2017 est. |
| — |
|
 Tokelau Tokelau |
|
1,000 |
|
1993 est. |
| 194 |
|
 Liberia Liberia |
|
900 |
|
2017 est. |
| 195 |
|
 Congo, Dem. Rep. Congo, Dem. Rep. |
|
800 |
|
2017 est. |
| 196 |
|
 Burundi Burundi |
|
800 |
|
2017 est. |
| 197 |
|
 Central African Republic Central African Republic |
|
700 |
|
2017 est. |
| 198 |
|
 Somalia Somalia |
|
N/A |
|
2017 est. |
|
World-Systems Theory, Dependency Theory and Global Inequality
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=79gCqjl6ihQ
In this video, I look at some of the causes of global economic inequality. Does World-Systems Theory and Dependency Theory offer answers, or are more nuanced explanations offered in works like The Bottom Billion and Why Nations Fail?
 Book: Why Nations Fail
Book: Why Nations Fail
Why Nations Fail: The Origins of Power, Prosperity, and Poverty, first published in 2012, is a non-fiction book by Turkish-American economist Daron Acemoglu from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and British political scientist James A. Robinson from the University of Chicago. [reference: Wikipedia]
 Book: The Bottom Billion
Book: The Bottom Billion
The Bottom Billion: Why the Poorest Countries are Failing and What Can Be Done About It is a 2007 book by Paul Collier, Professor of Economics at Oxford University, exploring the reasons why impoverished countries fail to progress despite international aid and support. [reference: Wikipedia]
Theories of Global Inequality
- development and modernization theory
- all countries need to be like ours
- dependency theory
- our system depends on cheap labor from the developing world
- world system theory
- capitalism does some things really well, but it needs control
Four Stages of Economic Development — Modernist Theory
- Traditional Stage — very little social
- Take-off Stage — period of economic grown accompanied by ...
- Technological Maturity — country improves in technology
- High Mass Consumption — a high standard of living the encourages consumption
- John: “if we stop Christmas, capitalism will collapse!”
Modernist Theory Beliefs
- Global inequality results from various dysfunctional characteristics of poor societies
- They lack a Western mentality: values that stress the need for savings, investment, innovation, education, high achievement, and self-control in having children
- People living in rich countries can best help poor countries by transferring Western culture and capital to them and eliminating the dysfunctions
- Only then will the poor countries be able to cap population growth, stimulate discovery
Dependency Theory Beliefs
- disputes that economic growth is the key to meeting important human needs in societies
- argues that the poor nations are caught in a cycle of structured dependency on the richer nations
- most often applied to the newly independent nations
Break
Video showed by DVD: Michael Moore film (starting at 5:31)
- “invasion” of Italy
- “there is no clash between the profit of the company and the well-being of the company” — CEO of Ducati
- benefits
- long vacations
- long lunch breaks
- numerous paid leaves
Do foreign investment and liberalized trade policies have positive or negative effects today?
- Modernization theorists want more foreign investment in poor countries and freer trade
- The strongly believe that following these policies will provide economic grown and general well-being
- They want trace and investment barriers to be dropped so free markets can ...
Foreign Aid: These countries are the most generous
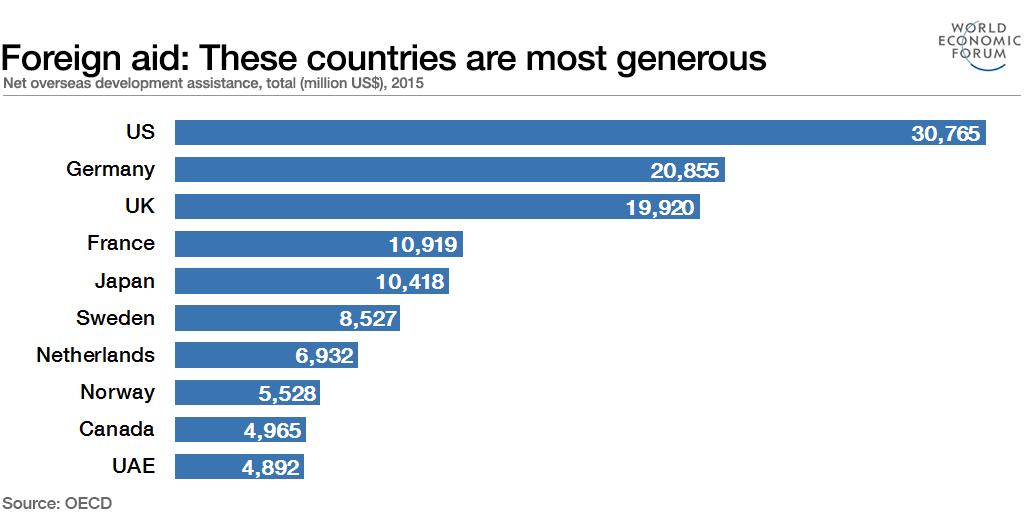
- US gives about 0.17% (2015) of Gross National Income
- Foreign aide is often accompanied by high administrative and overhead costs
- It is often given on condition that it be used to buy from donor countries goods that are not necessarily high-priority items for recipient countries
Debt Cancellation
- Many analysts argue that the world’s rich countries and banks should write off the debt owed to them by developing countries in recognition of historical injustices
- They reason that the debt burden of the developing countries is so burdensome that it prevents them from focusing on building economic infrastructure, improving health and education of their populations, and developing economic policies that can help them emerge from poverty
Tariff Reduction
- The reduction of tariffs by rich countries because these tariffs prevent developing countries from exporting goods that could earn them money for investment in agriculture, industry, and infrastructure
Democratic Globalization
- Research shows that democracy lowers inequality and promotes economic growth
- political stability is required for economic development
- Democracies make it more difficult for elite groups to misuse their power and enhance their wealth and income at the expense of the less well to do
- They increase political stability, so to provide a better investment climate
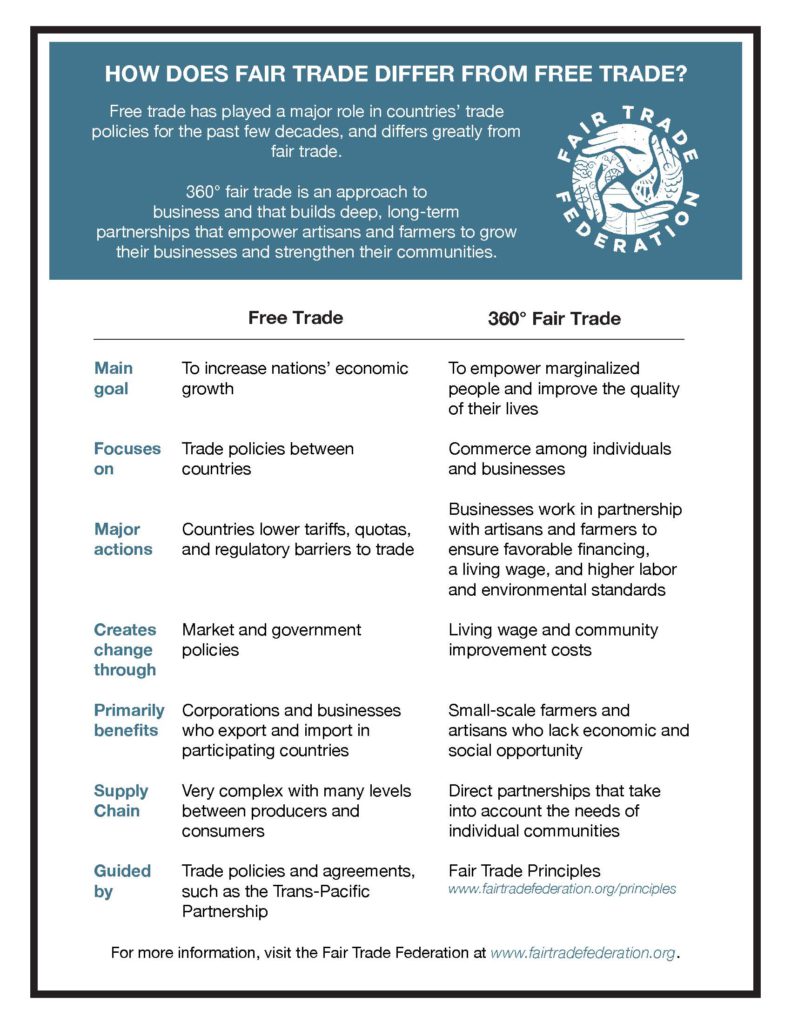
Fair Trade versus Free Trade
Wrap Up
- 19th cent. = Free Market Liberalism
- British invented capitalism
- this caused other countries to have to compete
- government required to promote economic development
- liberalism is great if you’re #1 or #2
- economies go through sets of stages
- when manufacturing jobs disappear, countries moved to services and finance
- finance is now perhaps the biggest, as demonstrated by earlier discussions
- $1T moves around the globe every day


Chad
Uganda
Zimbabwe
Yemen
Mali
Benin
Rwanda
Ethiopia
Solomon Islands
Guinea
Burkina Faso
Kiribati
Afghanistan
Sierra Leone
Guinea-Bissau
Haiti
North Korea
The Gambia
Togo
Madagascar
Comoros
South Sudan
Eritrea
Mozambique
Niger
Malawi
Tokelau
Liberia
Congo, Dem. Rep.
Burundi
Central African Republic
Somalia
 Book: Why Nations Fail
Book: Why Nations Fail Book: The Bottom Billion
Book: The Bottom Billion