
Notes on “Globalization and All That” Class No. 6
Links to Other Classes
Prev Class: No. 5 — Next Class: No. 7 — Index
Preliminaries
Important Announcement: Our scheduled Monday 11/19 class is canceled because John will be at a conference in Ireland
- thus, next week’s class will be our last
Numerous major events in the news this past week
- horrific synagogue shootings
- the mail bomber was caught
- Jair Bolsonaro was elected new president in Brazil
- he is generally considered to be to the right of Donald Trump
- NY Times: “Brazil on Sunday became the latest country to drift toward the far right, electing a strident populist as president in the nation’s most radical political change since democracy was restored more than 30 years ago.”
- Angela Merkel is stepping down in Germany
- this may make Brexit more difficult
- thus there are many big changes going on in the world at large
Remarks about the easy available of guns in the US
- Australia collected guns after a mass shooting there and there hasn’t been another such incident since
Reminder: Helter Skelter: A Presentation and Discussion on the Beatles’ White Album and the Impact of 1968
- Thursday, November 8, 2018
- 5:00 to 7:00 PM
- Lowell Telecommunications, 246 Market St., Lowell
- FREE!
Review and Continuation from Last Week
International Trade Post War - key features
- rapid growth as Europe, Japan and newly industrializing countries develop and rebuild
- growth of the MNC
- MNC = Multi-National Corporation
- build on Free Trade embodied in GATT and later WTO
- GATT = General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
- WTO = World Trade Organization
- facilitated by containers, technology and the global free trade regime
- development of regional trade blocs
Globalization and Interdependence
Regional Trade Blocs
- the US has signed more than 300 bilateral agreements and belongs to a number of regional trade agreements (RTAs) such as NAFTA
- NAFTA = North American Free Trade Agreement
- RTAs are often easier to form because fewer states are involved, which means fewer interests to reconcile
- many economist theorize that RTAs are a stepping-stone
Video: Episode 38: Trade Blocs (3 minutes 49 seconds)
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YDUq0DINhYk
- types (see 3:20)
- preferential trade area
- lower, but not eliminate, barriers among members
- free trade area
- eliminate internal barriers, but maintain independent external barriers
- e.g., NAFTA
- customs union
- eliminate internal barriers, agree on common external barriers
- common market
- e.g., East African Common Market, West African Common Market
- economic union, e.g., European Union
- full integration, e.g., United States
Liberal Philosophy: Trade is not only good in economic terms, but it bonds people together
North-South
- LDCs = less developed countries
- trade is an important growth of LDCs
- trade is controversial for LDCs, however, because of concerns regarding the distribution of the gains from trade (related to the terms of trade)
- LDCs don’t have sophisticated exports
- they have raw materials
- as opposed to value, which is added by manufacturing
- in the 1970s, a coalition of developing nations in the UN called the Group of 77 led the call for a new international economic order (NIEO) with conditions more favorable to the LDC -- including greater access for their primary commodities
- structure ____ policy: we’ll lend you money if you do X
Summing-Up on International trade
- trade has been used to serve national interests in many ways
- during the cold war, e.g., access to the US market was used as a “carrot” to entice allies away from communism
- trade sanctions and the threat of sanctions have also been used as a tool to punish nations that take foreign policy stands that the US opposes
- hurts the poor in these countries
- liberals applaud the WTO fr fulfilling the dreams of liberal officials who favor ...
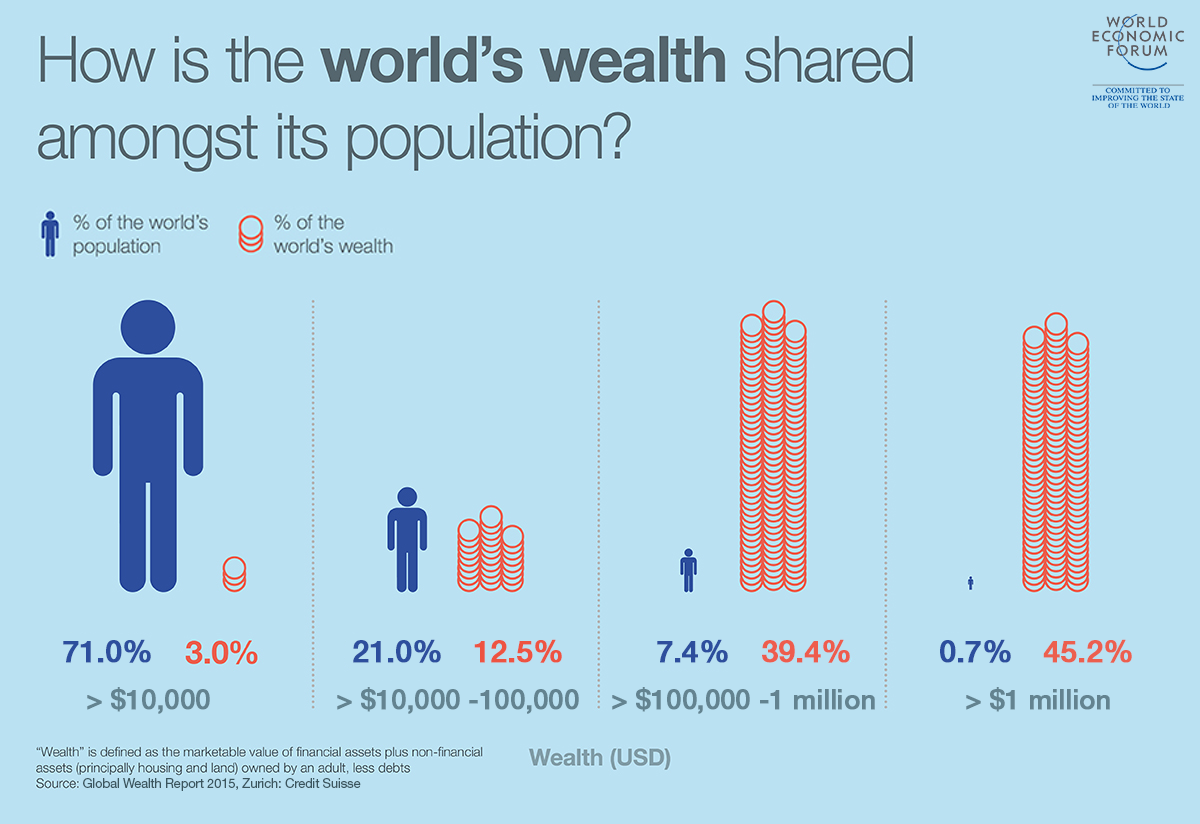
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2015/10/who-are-the-1-the-answer-might-surprise-you/
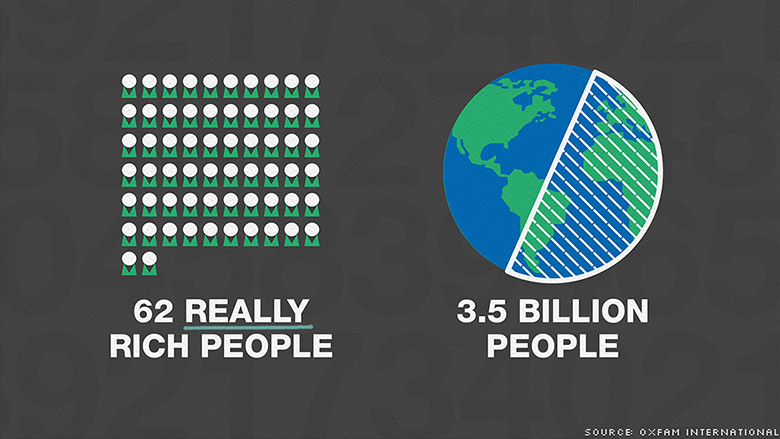
https://money.cnn.com/2016/01/17/news/economy/oxfam-wealth/index.html
Pros and Cons of Tariffs
- left argument
- protect workers (unions)
- protect communities
- start-ups (infant industries)
- small businesses
- liberal argument
- encourages competition
- innovation
- efficiency
- breaks down borders
- conservative argument
- increases state power
- protects domestic industry
- nationalist and mercantilism
- thus there are pros and cons in all philosophies
- if capital is global, domestic industry must think of innovation
The Multinational and Transnational Corporation
- MNCs have investment in other countries
- TNCs ...
- Mercantilist view: MNCs take on the identity of a state, pursue a state’s interests and generally act as an agent of a state in the global economy. Thus should be treated with suspicion because they are foreign agents.
- Revolutionary or revisionist view: MNCs control a state ...
- Liberal view: ...
MNCs: Definition
- Companies based in one state but operate globally, with fixed facilities and employees in several countries
- Types of MNCs:
- Industrial corporations: corporations that manufacture goods and sell them in various countries (e.g., cars, electronics)
- Financial corporations: banks that operate in several countries
- Service corporations: entities that provide services in several countries (e.g., telephone services, airlines)
- Apple is now the biggest company in the world in share market value
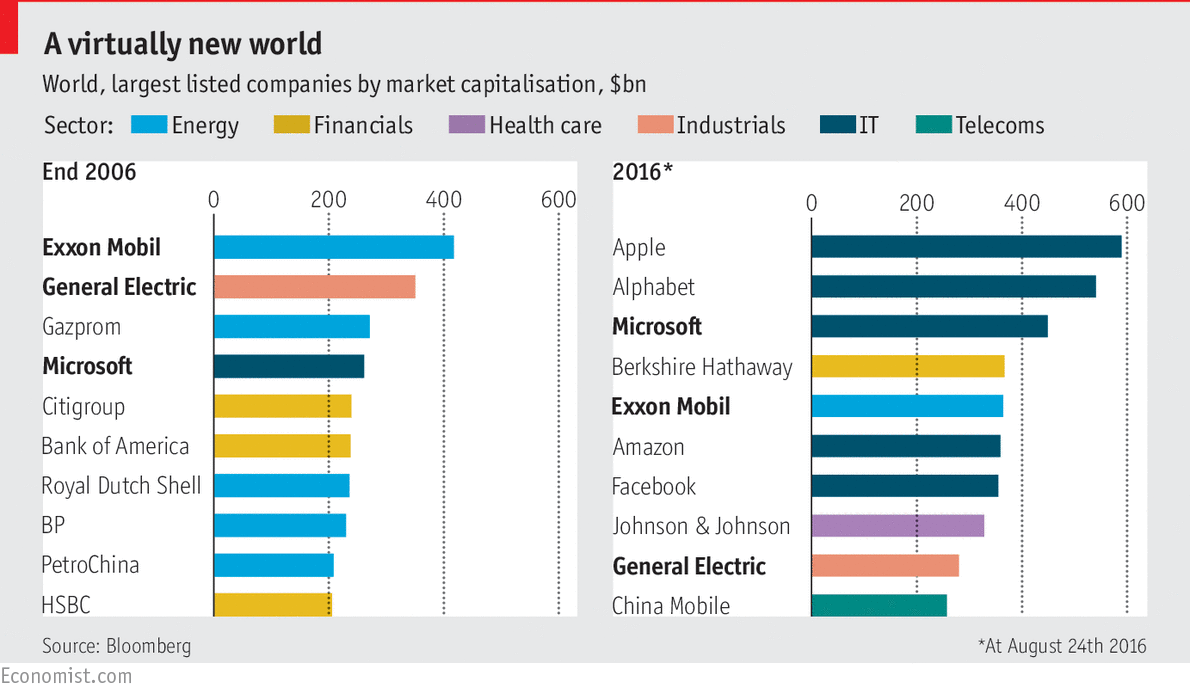
https://www.economist.com/special-report/2016/09/17/the-rise-of-the-superstars
Impacts of MNCs
- MNCs can have revenue of billions of dollars
- Push for global interdependence and a liberal world order
- having operations in different states, are interested in breaking down economic barriers
Robin Hood Tax
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZzZIRMXcxRc
- Bill Nighy video backing Robin Hood tax on banks = a spoof advertisement for this tax
- attempt to deal with debt of less developed countries
- small tax on developed countries to support less developed countries
Countries base on tax revenues
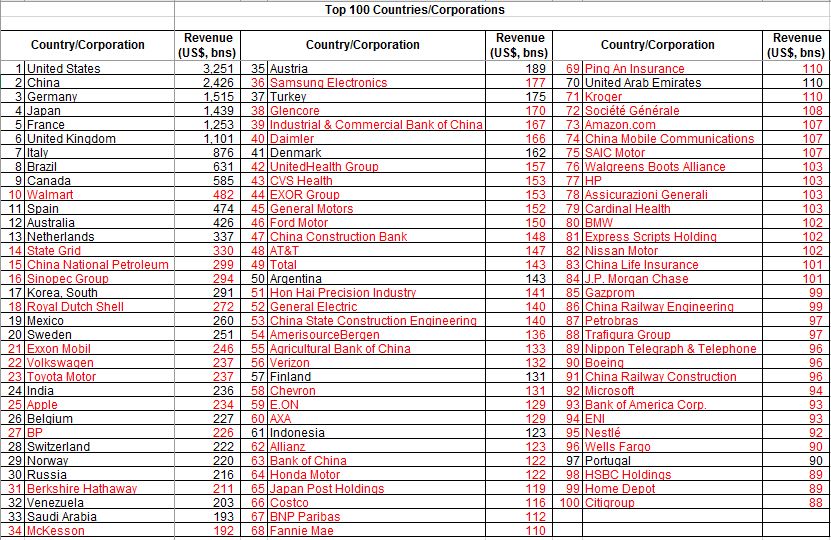
https://blogs.worldbank.org/publicsphere/world-s-top-100-economies-31-countries-69-corporations
John: “Capital has no country. Capital doesn’t like risk.”
Organization of MNCs
MNCs and Direct Foreign Investment
- MNCs are an important source of foreign direct investment (FDI) in countries. Investment is the act of exchanging money for the ownership of capital, mostly in the form of building, factories, vehicles, machinery.
- Such foreign investment in tangible capital, as opposed to investment in bonds, securities or currency is not portable. For the most part it is impossible to move factories out of a country.
- It is also part of a long-term commitment and strategy.
Attitudes Toward MNCs
Developing Countries and MNCs and FDI
- Economic nationalists in developing countries: while the FDI that MNCs bring is needed to develop the economy, there is the chance that it is the way for other countries to exploit and colonize the country, as was the case in the past ... So welcome the investment but worry that it comes at a high price in terms of long-term economic well-being and national security.
- It is also the means ...
- Thus, they often believe that FDI is a threat and should be eliminated.
- Liberals: FDI is good because it spreads economic activity across borders, spurs growth in all countries...
John Steward on Foxxconn — Fear Factory
Relation between MNCs and Governments
- Relations between and MNC and its home country can be complicated by the fact that the MNC has subsidiaries in particular countries that may or may not be friendly to the home country.
- Thus, an MNC may invest in a country that the home country wishes to isolate economically and politically; thus, it might be punished by the home country through fines, or its directors subject to criminal prosecution. For example, US companies that would try to create subsidiaries in Iran.
- John: "the alternative to free trade is fair trade”
- This relationship also might become complicated because of the actions of the home country or the actions of a host country.
- Decisions to base a subsidiary in a host country usually follows negotiations in which the MNC attempts to extract the most favorable terms possible from the host government in which the host government attempts to lure the MNC to invest and the MNC threatens to take its investment elsewhere unless favorable conditions are created, such as
- favorable tax treatment
- ...
Sources of Conflict between MNCs and Host Countries
Post WWII Developments — Many Crises
- 1982: Mexican Debt Crisis
- 1985: Savings and Loan Association Crisis (in US)
- 1989: Japanese asset bubble burst
- 1991: Bank of Credit and Commerce International (BCCI) scandal = biggest banking fraud ... lack of regulations
- 1992: Maastrich Treaty — EU and Euro
- 1994: Financial Crisis in Turkey
- 1995: Barings Bank fails for a second time
- 1997: East Asian Financial Crisis
- 1998: Russian Financial Crisis — catastrophic
- 1999: Brazilian Crisis
- 1999: Eleven European countries introduced Euro as an accounting currency
- 2001: Turkish Financial Crisis
- 2005: China emerged as a major player in the global financial system
- 2006: Problems in the US mortgage market
- 2007: US Mortgage Crisis and Recession
- 2008-15: Global Economic Crisis
- Massive loss of wealth, near collapse of Portugal
Thomas Jefferson 1802 quote
I believe that banking institutions ...
Global Financial Deregulation
- from 1973 we see fairly rapid “deregulation”by major states
- three aspects
- deregulation of particular national markets
- removal of controls separating functionality distinct markets ...
Changing Financial System
- massive increase in volume of trading across different markets
- daily volume of share trading on the NYSE
- 1970 = 10M
- 2005 = 1B
- 2018 = 1.5B = daily trade of about $30B
- all stock markets = $1.7 trillion/day
- high levels of volatility
- early 2000s DJI lost half its value
- values of major currencies fluctuate 50-100%
- finance itself becomes a critical industry
- between 1/4 and 1/3 of UK employees are involved in Finance
- cultural normalization of debt
Rapid Deregulation & Globalization
- 1970s: Financial deregulation of banks & offshore banking
- 1980s: Globalization of the bond markets
- 1990s: Globalization of banking & equity markets
- 1995: Globalization of trade under WTO
Discussion
- we covered history and how we think of the global financial system
- the financial system developed as a reaction to the World Wars
- next week we’ll look at the inequities of that system


