
Notes on “Globalization and All That” Class No. 5
Links to Other Classes
Prev Class: No. 4 — Next Class: No. 6 — Index
Preliminaries
Helter Skelter: A Presentation and Discussion on the Beatles’ White Album and the Impact of 1968
- Thursday, November 8, 2018
- 5:00 to 7:00 PM
- Lowell Telecommunications, 246 Market St., Lowell
- FREE!
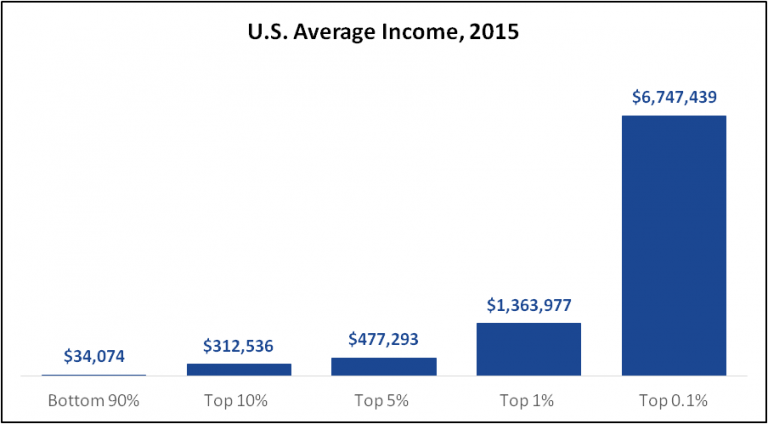
Average Income
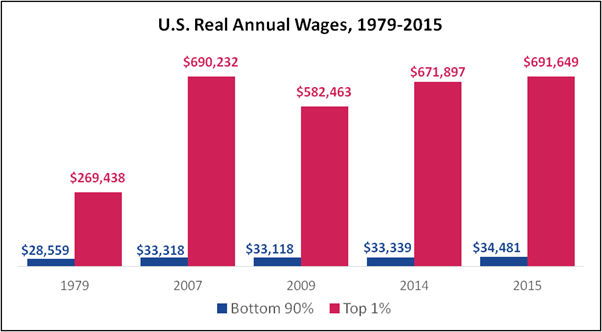
Annual Wages
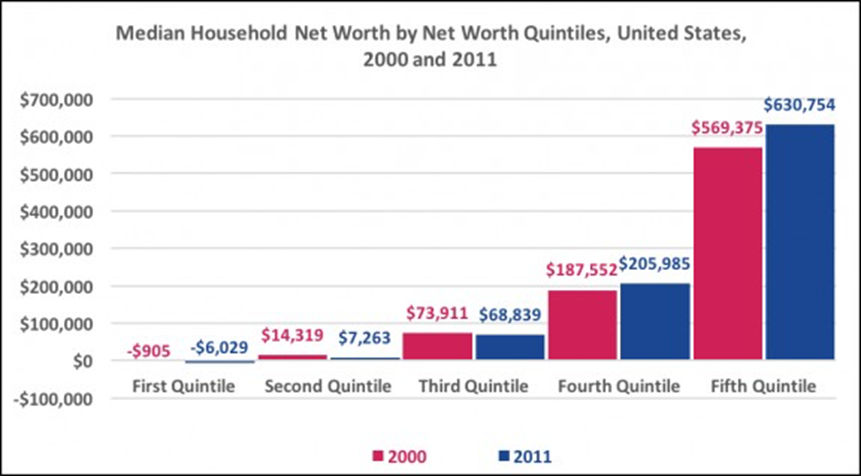
Household Net Worth
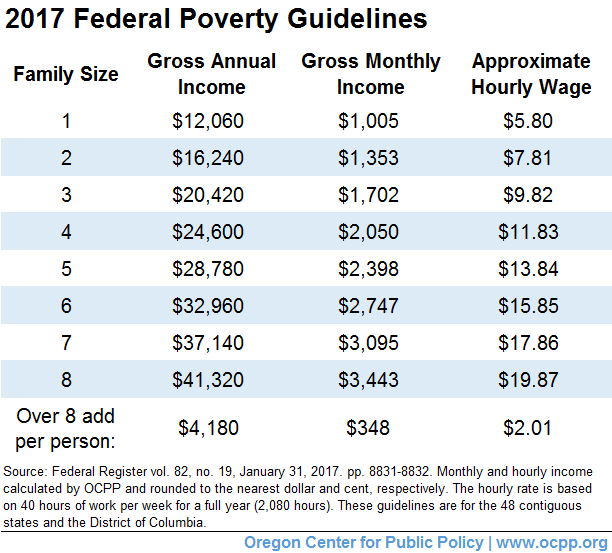
Official Federal Poverty Level Rates
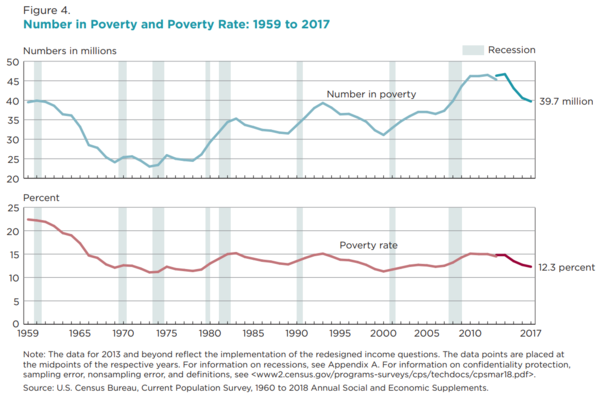
US Poverty Rates

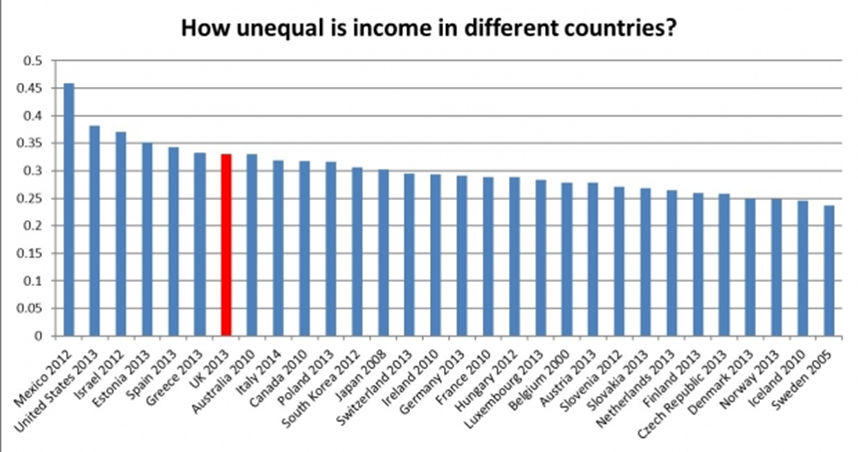
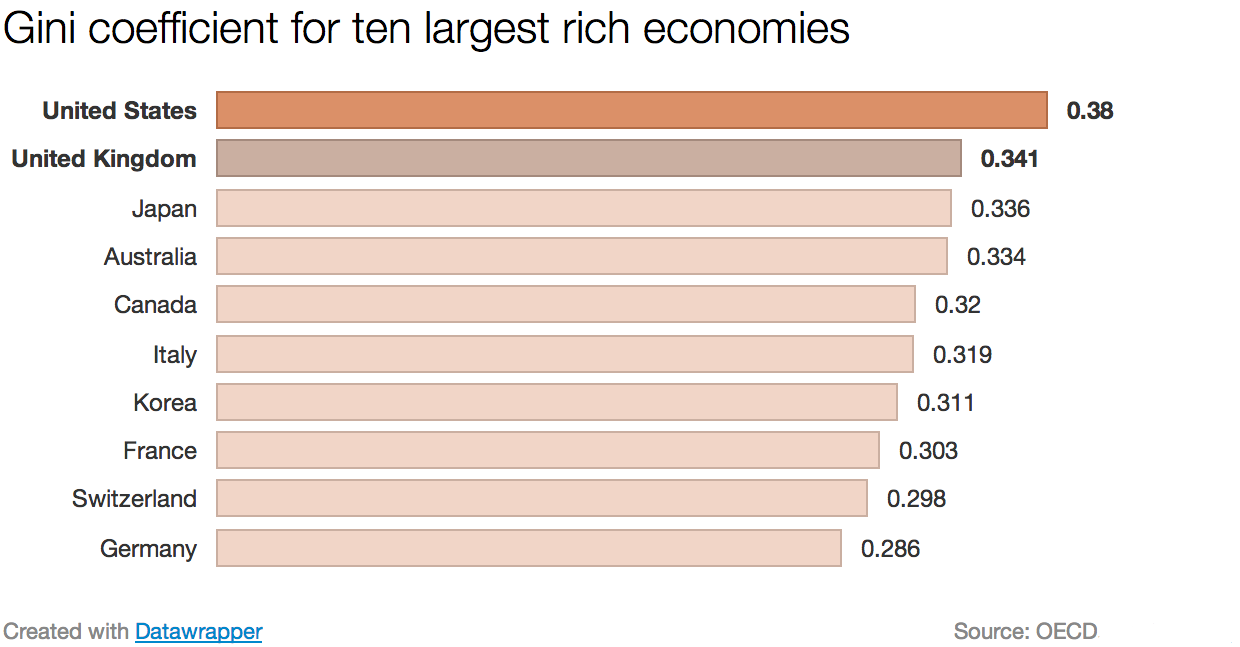
World Income Inequality by Gini Coefficient
- note that countries with lower coefficients generally tend to have extensive welfare systems
Review and Continuation from Last Class
Economic Response to assumed causes of WWII
- stabilize financial system
- reduce tariffs
- develop and promote liberal ideas and values
Major Take-Aways
- Bretton-Woods System created in 1947
- Entwined Politico-Strategic and Economic Developments 1945-1971
- US economic dominance under Bretton Woods
- creates GATT
- IMF, World Bank, and other international institutions
- sets of system of fixed exchanged rates
- dollar is reserve currency based on gold
- acceptance of Keynesian intervention to manage economic recessions
- Cold War
- pre-emergence of Western Europe - the EEC - EC - EU, and Japan
- decolonization - third world, Cold War competition
- rise of the multinational corporation (MNC)
- emerging economies
- liberal reform and social democracy in Europe
- Vietnam War and inflation
1971 Nixon ends Bretton Woods - “New Economic Policy”
- Nixon sets tax cuts and a 90-day freeze on prices and wages
Post Bretton Woods
- After the collapse of the Bretton Woods system, the major powers authorized the IMF to widen the trading bands so that changes in currency values could more easily reflect the supply and demand of currencies.
- The oil shocks of the 1970s helped preserve the dollar’s status as top currency, as OPEC demanded ever-greater quantities of dollars to purchase OPEC oil.
- OPEC nations placed many of these “petrodollars” in Western banks.
- Petrodollars were loaned out to developing countries, which substantially increased their debt.
1970s
- Arab/Israeli conflict, OPEC and global economic crisis
- inflation “stagflation”
- crisis in Europe - Cold War and Eurocommunism
- Expansion of US and now other MNCs
- shift from manufacturing to service economies in the West
- changes in political power bases domestically in the US
- all of this drove us toward Thatcher/Reagan and neo-liberalism
- similar to what Trump is saying today
- return to the liberalism of the 19th century
- minimal government intervention
Setting the Stage for the next phase of globalization
- stagflation (concurrent inflation and slow economic growth) during the 1970s prompted the US to raise interest rates to combat domestic inflation, which contributed to to global recession
- IMF structural policies = new-liberalism as defined above
- this economic downturn motivated a turn away from Keynesian orthodoxy in favor of a return to classical liberal ...
The
Global Financial and Monetary System
Review of Foreign Exchange cartoon
- (Macro) Episode 33: Exchange Rates
- the value of your currency has a great effect on how you trade
- remember that a great deal of money is exchanged every day
- building a foreign exchange reserve saves money by eliminating exchange fees
- these enable you to buy and sell your old country
- you increase the value of your currency by buying it with foreign currency
Old vs. New Trade Theory
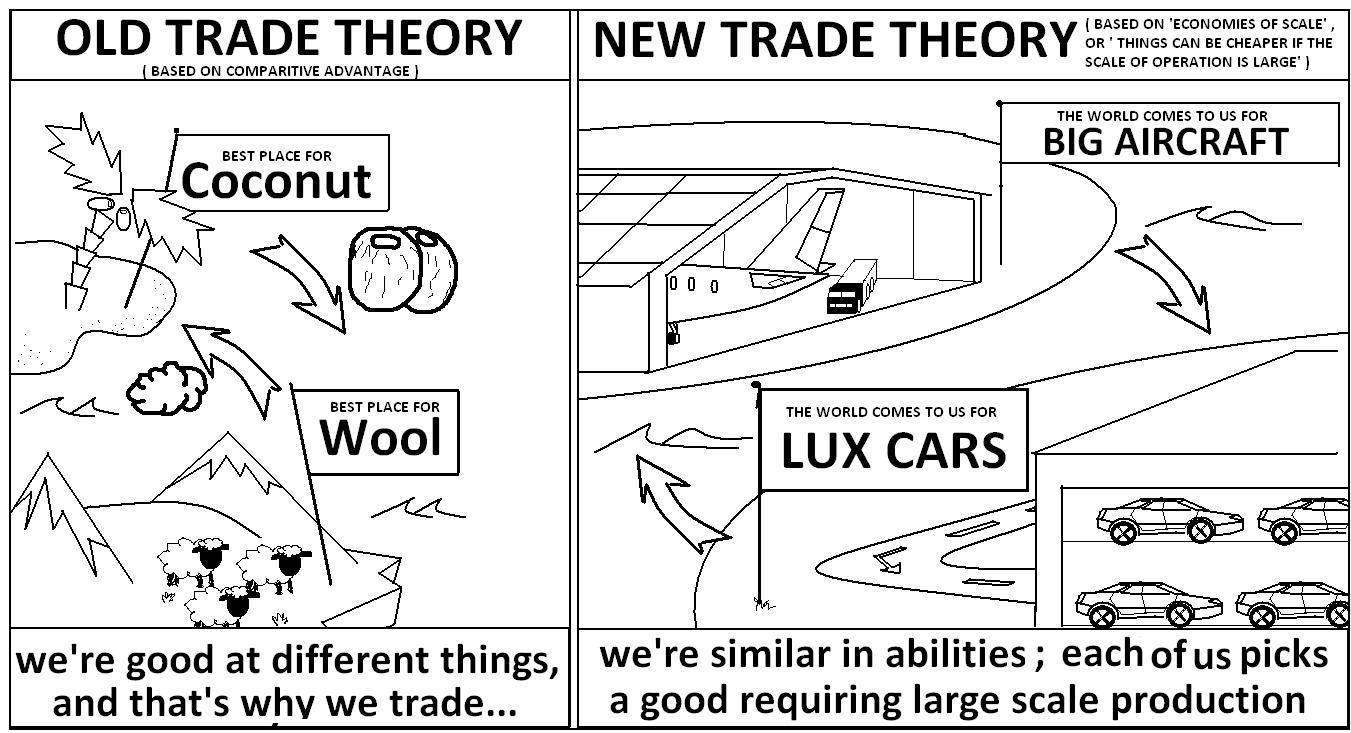
International Trade
Theory of Absolute Cost Advantage — basically, Adam Smith
- producing a good with fewer inputs (capital, labor, land, raw materials, etc.) per unit of output than other countries
- if input prices are ...
Theory of Absolute Cost Advantage — Ricardo
- focus on comparative cost advantage not on absolute cost advantage
- each country specializes in the production of that commodity in which it’s competitive...
Factor Endowment Theory — Crosscheck and Ohlin
- “a country will export goods that use its abundant factors intensively, and import goods that use its scarce factors intensively” (Wikipedia)
Theory of Competitive Advantage — Michael Porter (MIT Economist, MacArthur Award recipient)
- to compete in the world a country requires a strategy to gain a competitive edge over the others
- competitive advantage is created by technological and institutional change, not just inherited from a country’s natural endowments
- for example, getting really good at making photovoltaic cells
Product Life Cycle Theory — Vernon
- industrialized countries contribute more resources to R&D, which results in development of new products in that country
- in early stage they have monopoly on such new products and enjoy easy access to foreign markets — think US computers
Theory of Identical Preferences — Liner
- based on the principle that trade opportunities are more among countries at similar stage of development with similar demand structure
- e.g., USA and Japan are largest trade partners because of identical consumer preferences and similar stage of development
Product Differentiation
- another reason or basis for international trade can be the product differentiation
Outlet for Surplus
- most countries involve in international ...
who.org/ statistics trade
Globalization and Trade
Globalization is about mobility and speed to stretch beyond political boundaries
- technologies of mobility
- ideas of mobility
- capitalism
- requires efficiency for economic competition
- efficiency requires mobility
- ... speed
Post 1970s Neo-Liberalism
The underlying causes of the current phase of globalization ...
Break
N.B. It is easier to manage the system in Scandinavia because there are far fewer people
- e.g., 6 million in Scandinavian countries vs. 350+M in US
- also, US culture is more anti-government than in most European countries
- e.g., public transportation can’t make a profit
- e.g., if 10% people on welfare are scamming the system, that’s nothing compared to what hedge fund managers walk away with
Old Bretton Woods institutions are being challenged
- old arrangements are relics
- In IMF and World Bank, Benelux has a larger quota than China
- China challenges the “Washington Consensus”
= promotion of neo-liberalism on a global scale
- why should it be the premise for economic development
- and a condition for loans?
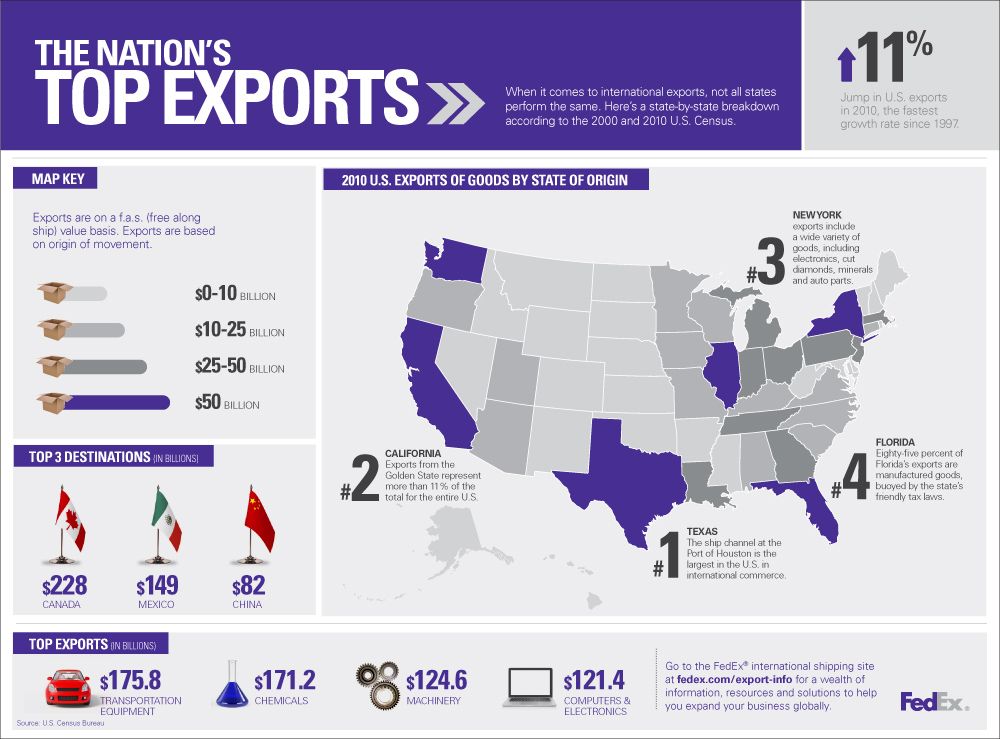
Who trades with whom?
US Trade Imbalance
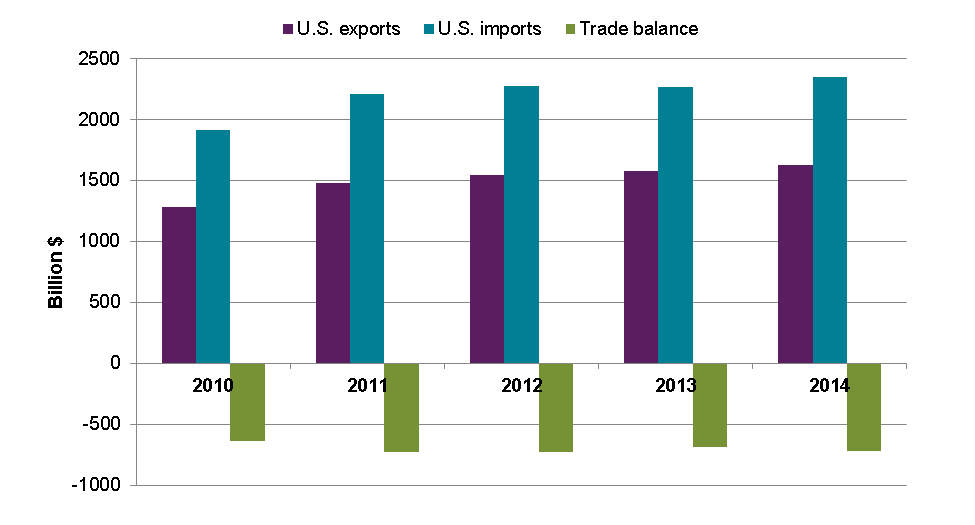
Trade
- the production and trade structure ...
Where Boeing 707 components are made
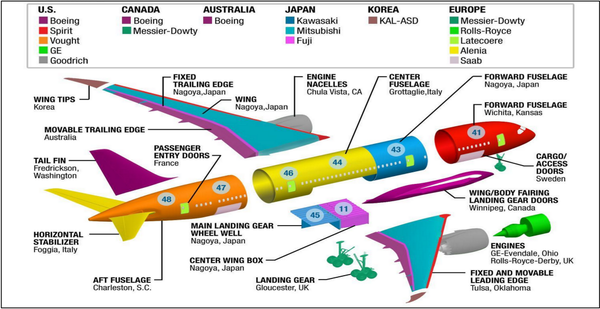
Trade
- due to capital mobility, foreign direct investment has grown — through most of it is still concentrated in the already-developed nations
- the expansion in international trade is a reflection of the internationalization of production processes
- trade promotes social, political, and economic interdependence between trading partners
- int he absence of comprehensive and binding international trade rules, tensions between trading partners are likely as states try to maximize domestic gains from trade, often at the expense of trading partners’ welfare
Post-War Target Regimes
- GATT = General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
Trade Regimes
- mercantilism on the rebound
- protectionism increased among industrial nations in the 1950s and 1970s due in part to declining US hegemony, the rise of Europe and Japan, and changing patterns of global production
- the Tokyo GATT Round attempted to deal with a growing number of non tariff barriers (NTBs) and other discriminatory practices such as dumping
- In the 1980s trade accounted for a increasingly higher percentage ...
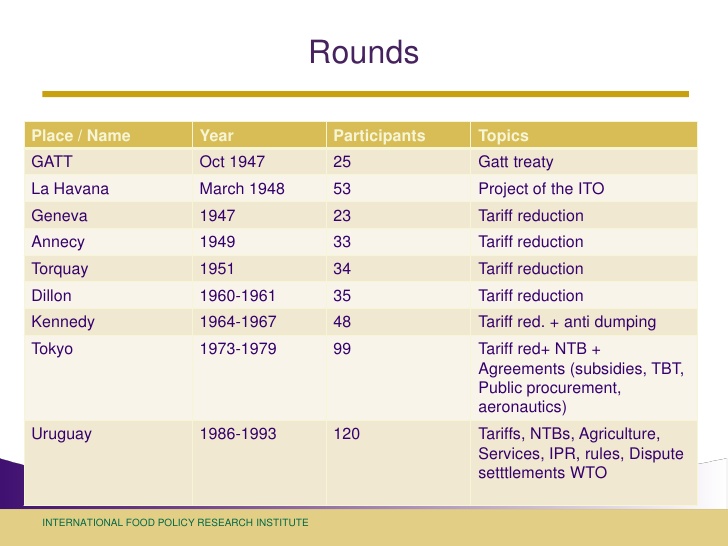
Quick and Dirty History of GATT Rounds
- goal = trade tariff reduction
- VEC = Voluntary Export Controls
- GATT evolved into the WTO = World Trade Organization
Take-Aways
- there’s always a way to get around something
- are tariffs good or bad? — a very complex question
- it’s way more complicated than the current administration is making it out to be
- many jobs of course disappear due to technology, not cheaper labor
- discussion of paying everyone a minimum wage
- John (personal experience): “someone built a hallway in which there were a lot of doors to be opened”


