UMass Lowell Dept. of Computer Science
COMP 4620 — GUI Programming II
Spring 2016 Semester, Section 201
Prof. Jesse M. Heines
Notes for Class No. 3
Discussion of Project Planning Statuses and Getting Started with MEAN
Tuesday, January 26, 2016
A video of this class is (or will be) posted at:
http://echo360.uml.edu/heines2016/comp4620-201.html
Handouts and Materials
Openings / Announcements / Reminders
As of 8:45 AM this morning (Tuesday, January 26th), 36 of the 39 students enrolled in this course had completed the form at:
https://docs.google.com/forms/d/166cx_uRhYJ24qoI-zMrs1dpWVyOw5iloQ-ojjF41lv4/viewform
- if you’re one of the 3 who has not, please do so immediately
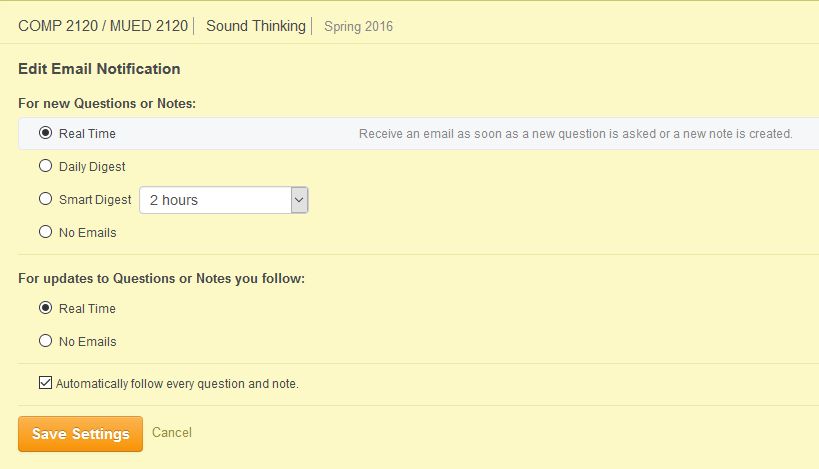
Also remember to set your Piazza Account/Email Settings under Edit Email Notification:
- select Real Time under both “For new Questions or Notes” and “For updates to Questions or Notes you follow”
- in addition, check the Automatically follow every question and note checkbox
- then click the Save Settings button
Article posted by Curran Kelleher
https://data.triplebyte.com/who-y-combinator-companies-want-c1880a08ac88#.3wrgrd9i3
As asked on Piazza: What is a “Y Combinator company”?
- Y Combinator is an American seed accelerator, started in March 2005. Forbes has found YC to be the most commercially successful seed accelerator in the world. [Wikipedia]
- Wired magazine has called Y Combinator a “boot camp for startups” and “the most prestigious program for budding digital entrepreneurs.” [Wikipedia]
- An accelerator and venture capital company that does seed, early stage venture, and debt financing investments. [CrunchBase]
- https://www.ycombinator.com
- Thus, a “Y Combinator company” is a company whose founders or leaders have been supported by Y Combinator.
Patterns observed in their study
- There’s more demand for product-focused programmers than there is for programmers focused on hard technical problems.
- (Almost) everyone dislikes enterprise programmers.
- We don’t agree with this. ... But it’s what our data shows.
- Experience matters massively.
Conclusions
- YC Startups disagree strikingly about who’s a good engineer.
- Each company brings a complex mix of domain requirements, biases, and recruiter preferences. Some of these factors make a lot of sense, others less so.
- But all of them are frustrating for candidates, who have no way to tell what companies want.
Where do we stand on project ideas and partnerships?
- who is not yet in a group?
Class Notes
Related reading for this class: Writing Handouts and GetMEAN: Chap. 3
Getting Started with MEAN — Textbook Ch. 3
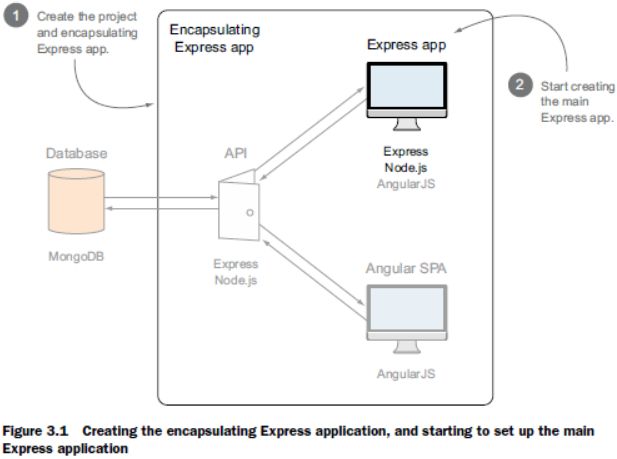
“Express is a web application framework for Node. In basic terms, an Express application is simply a Node application that happens to use Express as the framework.” (p. 55)
Step 1: Installing the pieces
- see Appendix A, p. 391, for instructions on installing all MEAN stack components
- see Appendix B., p. 395, for instrictions on installing Git and setting up Heroku
Step 2: Create a project folder (p. 58)
Step 3: Create the Express application (p. 59)
Step 4: Explore the directory structure
Step 5: Explore the package.json file (pp. 55-60)
- what is the format of this file? why?
- the first part contains various metadata defining the application
- the second part lists the dependencies needed for the application to run
- dependency versions are specified as:
Major.Minor.Patch
- “Prefixing the whole version number with a ~ is like replacing the patch version with a wildcard, which means that the application will use the latest patch version available. This is considered best practice, ...” (p. 56)
Step 6: Installing Node dependencies with npm
Understanding the workflow (p. 60)
- create an HTML template that includes placeholders for data
- pass it some data
- the template engine compiles these two together to generate HTML that is sent to the browser to render
- example: the Teaching page on my website
Understanding Jade (p. 60)
- Jade does not contain any HTML tags
- instead, it uses “tag names, indentation, and a CSS-inspired reference method”
- if a tag name is omitted, Jade assumes you want a DIV tag
- “Jade templates must be indented using spaces, not tabs!”
Example Jade code
#banner.page-header
h1 My page
p.lead Welcome to my page
Resultant HTML output
<div id="banner" class="page-header">
<h1>My page</h1>
<p class="lead">Welcome to my page</p>
</div>
Step 7: Testing the project (p. 61)
- make sure you are in the topmost directory of your application
- open your browser and enter
localhost:3000 in the address bar
Step 8: Using nodemon (p. 64)
- then type
nodemon in the topmost directory of your application
- open your browser and enter
localhost:3000 in the address bar as before
- the only difference is that when you change a file, Node will restart automagically
JMH Learning Tricks
- Add your name to the
views/index.jade file
- Add a timestamp as a page footer
- note that Jade comments can only be written in // style
Assignment No. 1 Expectations
Review of Assignment No. 1 requirements
Balsamiq Mockups — GUI design tool
For Macs, 2014 student Rob Cadwallader recommends OmniGraph
- the download is a
.dmg file, so it does not work on Windows
- I believe the download is a 14-day trial version, but I’m not sure
Writing Expectations — Using Word Like a CS Major
page settings
- title page
- headers and footers
- automatic generation of tables of contents
using styles
paragraph settings
- lines per inch
- indentation
- space after
- justification
- borders and shading
- widow line control
- “keep line with next”
- widow heads
using lists
- bulleted
- numbered
- outline numbered
proper use of fonts
proper use of spaces and tabs
- types of tabs
- dots and lines
- adjusting default settings
inserting and manipulating graphics
- working with screen captures
- labeling tables and figures
inserting and numbering code
citing references